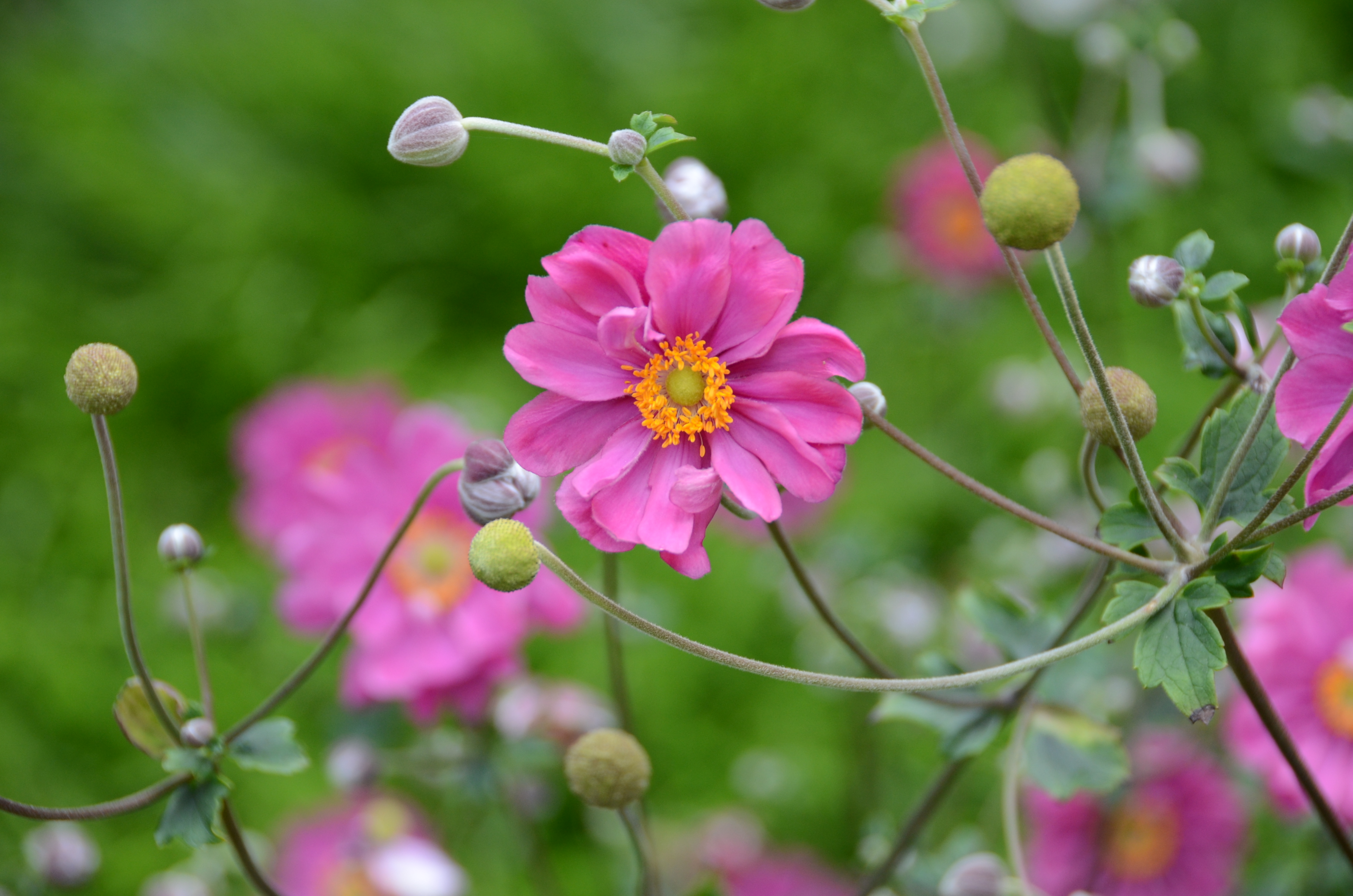
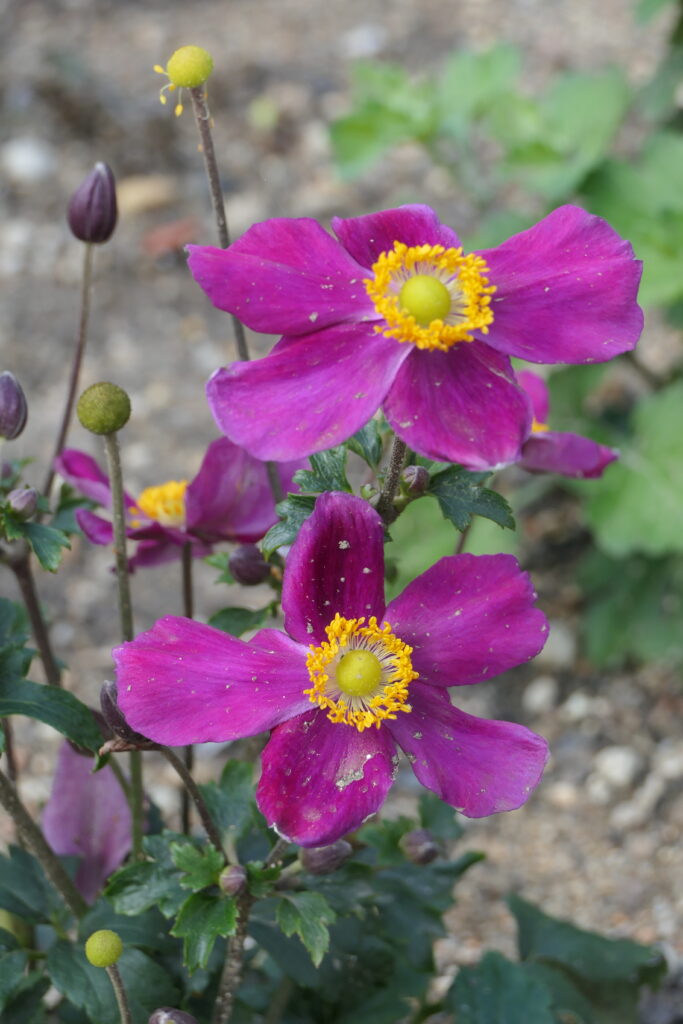
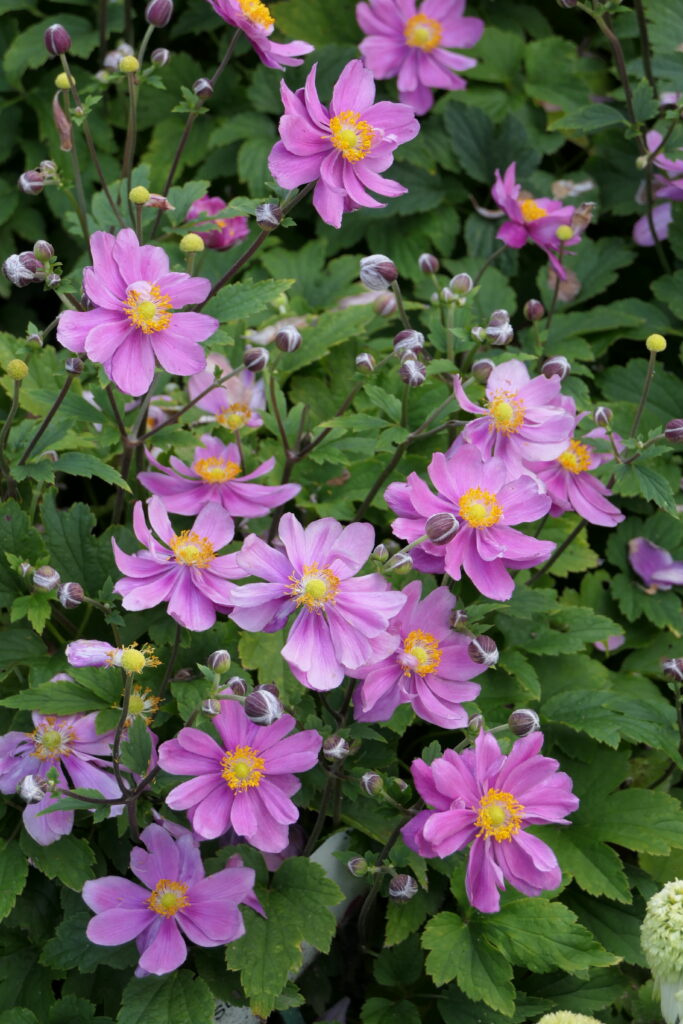
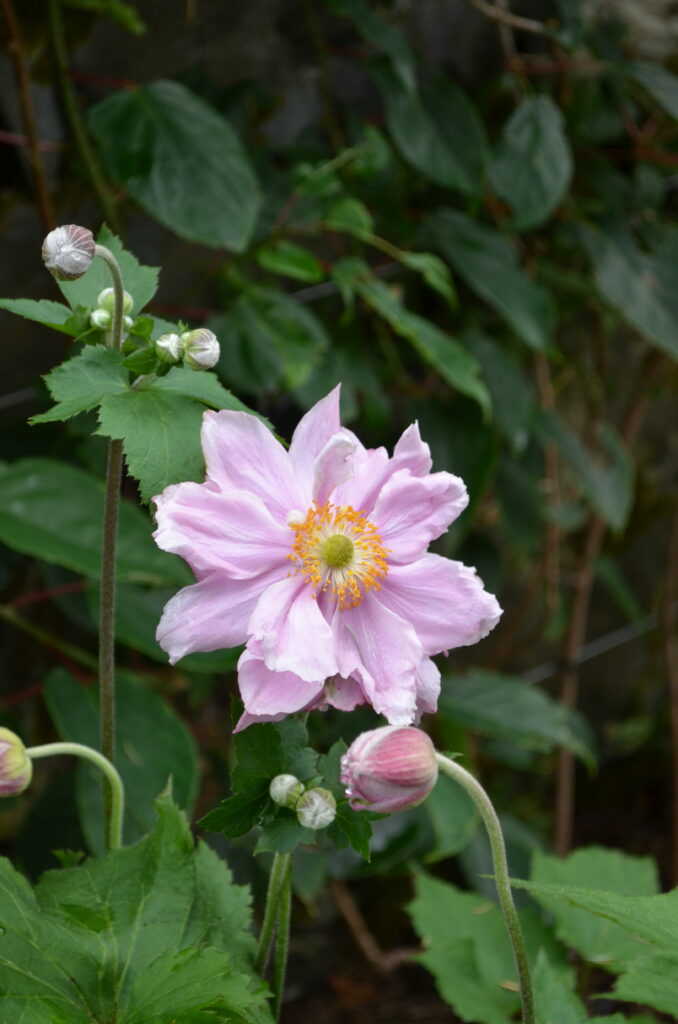
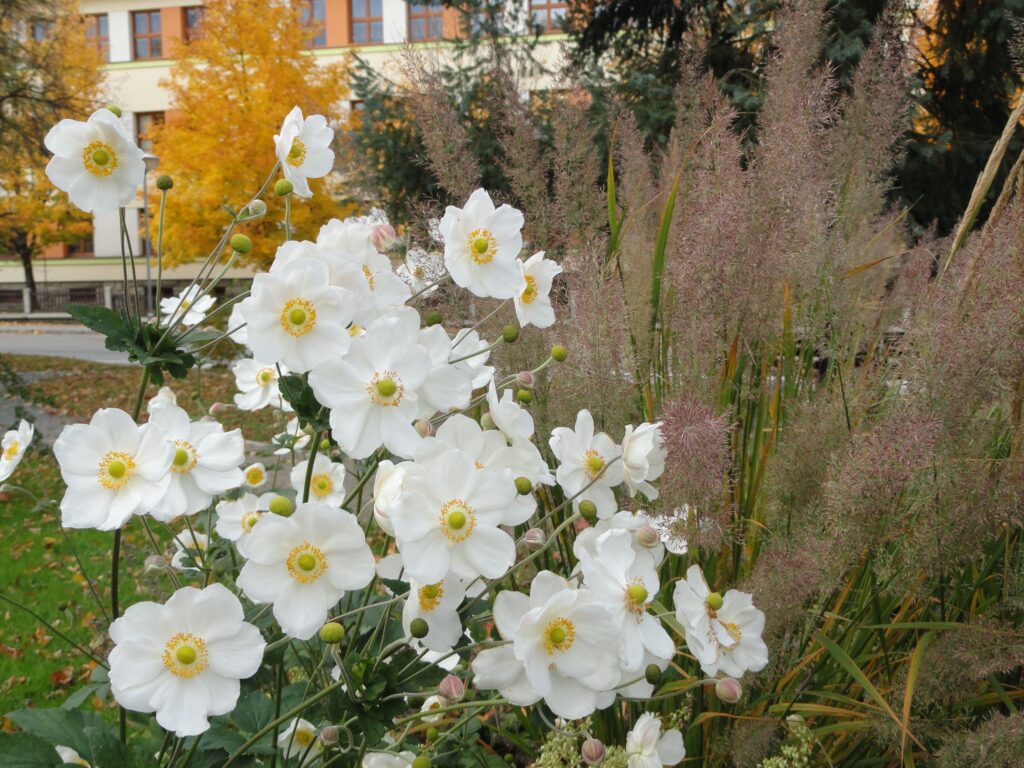
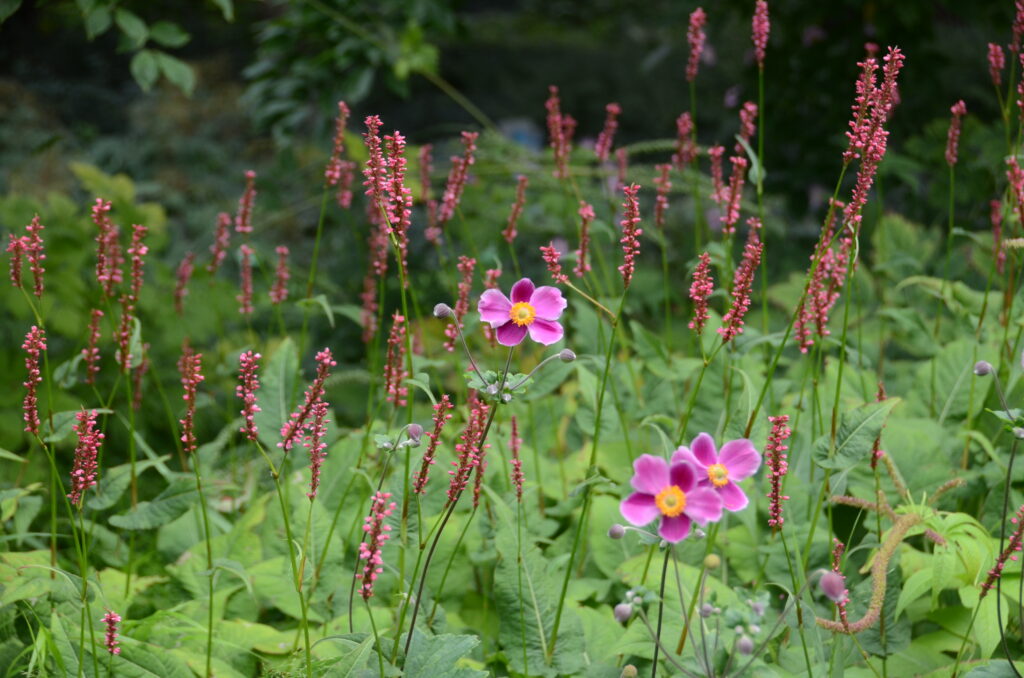
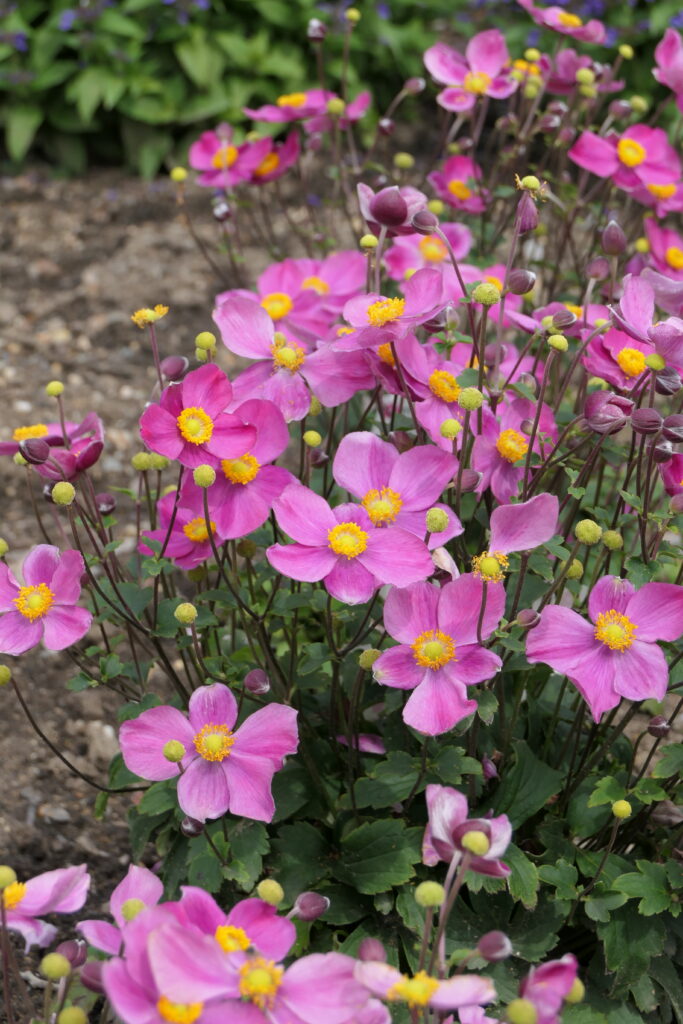
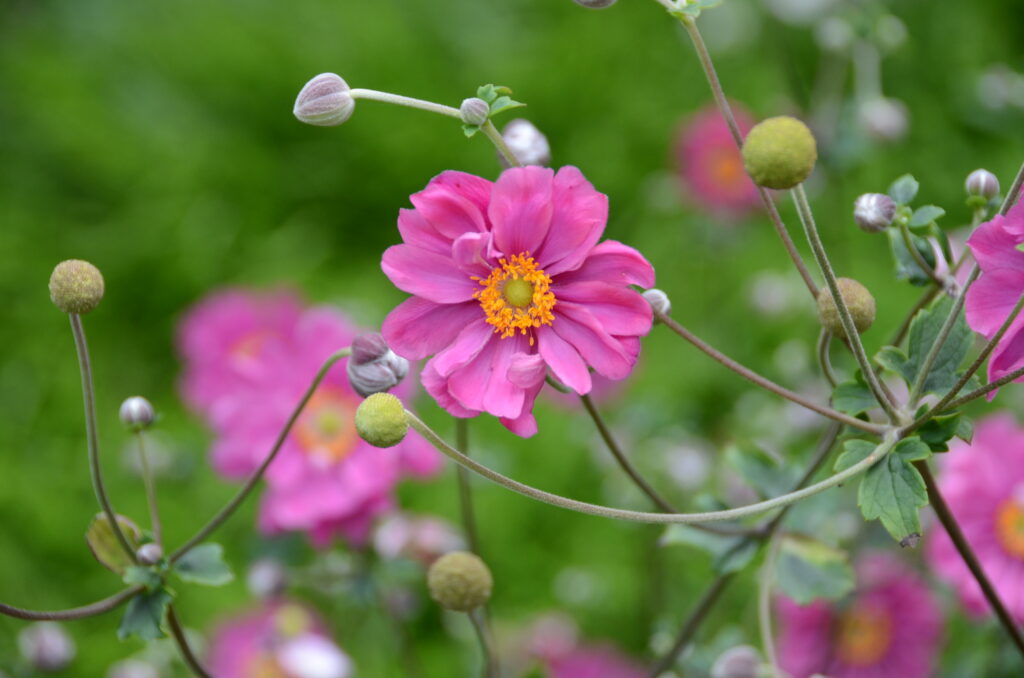
From a genus rich in species Anemone (family buttercup, around 120 species) belongs to the group of autumn-blooming anemones the most attractive garden perennials of this period. They are quite incremental, picky plants with a height of 0,6 when 1,5 m, which from bundle roots, through underground outcrops, they grow further into larger stands. From mid-summer then from ground rosettes, long-petioled, divided leaves grow flower-bearing stems. They carry distinctive, big flowers in white, pink and crimson shades, which gradually bloom until freezing.
In garden culture, anemones appear from 17. stol. in east asia. They were imported to Europe in the first half of. 19. a table from China. This is where the origin comes from. kind of Anemone hupehensis (syn. And. there is japonica. hupehensis), which here grows on slopes in gorges, between wet stones, in the undergrowth or in the open, rocky habitats in the heights 600-2500 m above sea level.
Since the beginning of cultivation, gardeners have tried to obtain new ones varieties of anemones, different mainly in the color of the flowers and the number of petals (single nebo double). Currently it is several dozen varieties available in production. Derived from the original species are e.g. ´Pink Saucer´, ´September Charm´, ´Praecox´, 'Prince Heinrich'. Under the name Anemone x hybrid many other varieties derived from crossbreeding are sorted And. vitifolia a And. hupehensis var. japonica, e.g. ´Andrea Atkinson´, ´Hadspen Abundance´, ´Honorine Jobert´, ´Lady Gilmour´, ´Loreley´, ´Pamina´, ´Whirlwind´. The most hardy of the winter anemones is And. tomentosa ´Robustissima´.

Anemones are best suited to a semi-shaded, moist location, permeable humus soil, where they complement well with other autumn species perennial such as. limit (Aconite) or a bed bug (Cimicifuga). Second it is possible to plant anemones in open habitats or in classic ones perennial beds, where they stand out well in contrast with the planting autumn species of grasses and asters. Anemones do not suffer much from diseases and pests. Varieties are propagated by root cuttings, botanical species and sowing.